The housing affordability crisis has emerged as a formidable challenge for millions of Americans, trapping them in a cycle of escalating costs and diminishing access to homeownership. Despite soaring productivity in various sectors, the housing market trends reveal a stark contrast, making the dream of owning a home increasingly elusive. Factors such as soaring labor and material costs, compounded by the stifling effects of NIMBYism and stringent land-use regulations, have resulted in a dramatic decrease in construction productivity. This complex web of homeownership challenges underscores the critical need for innovative solutions to revitalize the housing market and make homes affordable again. As we delve deeper into this pressing issue, it becomes evident that addressing these obstacles is crucial for achieving a sustainable future in housing.
At the heart of America’s economic turmoil lies a significant issue: the struggle for affordable housing. As the real estate landscape evolves, many find themselves grappling with the repercussions of restrictive zoning laws and community opposition to new development, often referred to as NIMBYism. The broader implications of these challenges stretch into the realm of construction efficiency and land-use policies, derailing progress and innovation in building homes. Increasing home prices have made the prospect of homeownership a distant reality for a considerable portion of the population. Recognizing and addressing these interlinked issues is paramount in steering the nation toward a more accessible and equitable housing environment.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
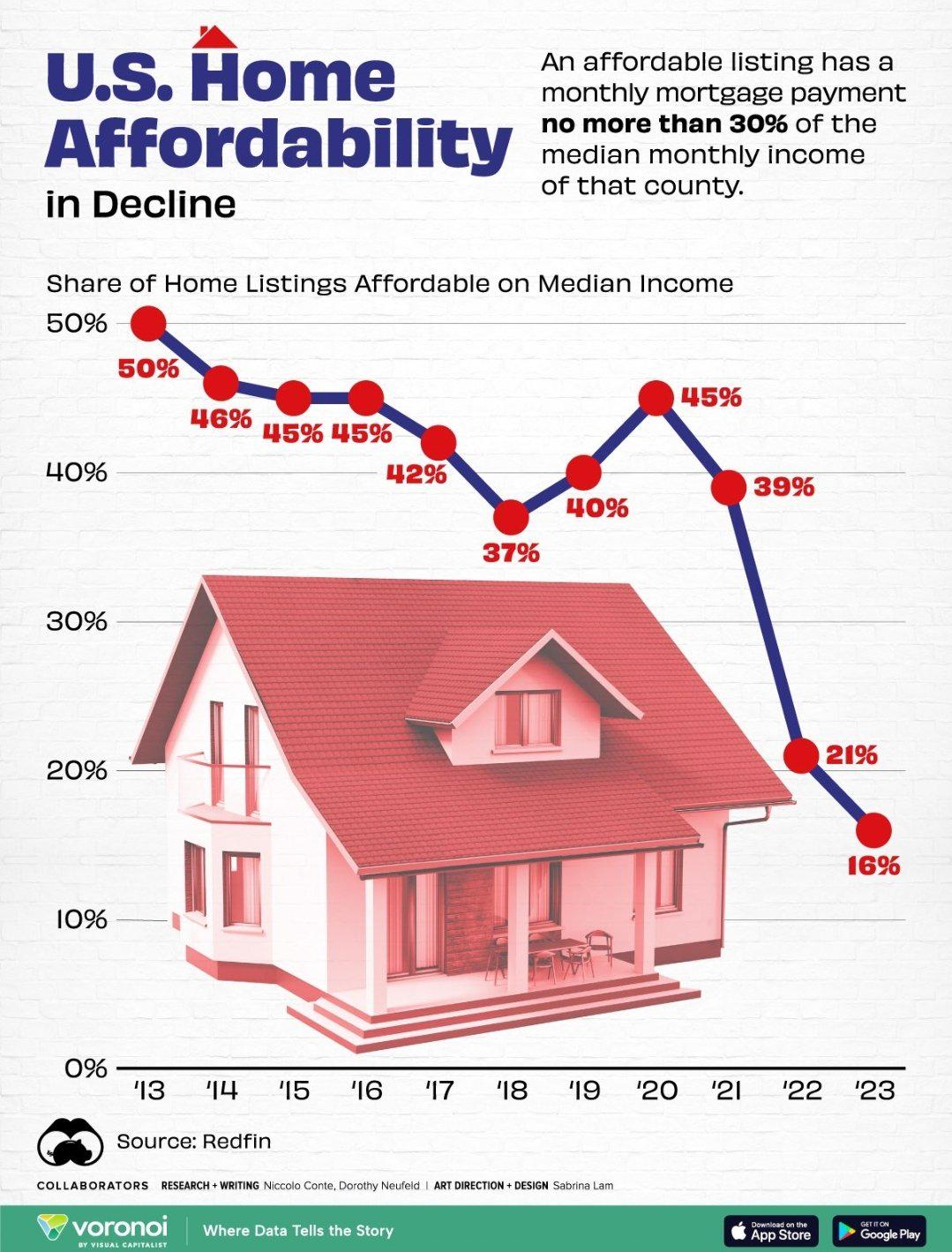
The housing affordability crisis has become a pressing issue in contemporary America, as skyrocketing home prices and rising rental costs contribute to a growing disparity in homeownership opportunities. This crisis is particularly affecting younger generations and low-to-moderate income families who find it increasingly difficult to secure affordable housing. According to recent studies, the average cost of a single-family home has more than doubled since 1960, raising concerns about the long-term socioeconomic implications of such trends.
Factors contributing to this crisis include increased labor and material costs, as well as stringent land-use regulations that inhibit construction innovation and the development of large-scale housing projects. The complex interplay between governmental policies and market dynamics has created barriers that prevent builders from meeting the rising demand for affordable housing, leading to a situation where homeownership feels unattainable for many.
The Impact of NIMBYism on Housing Development
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My BackYard’ mentality, has profound implications for the housing market and exacerbates the affordable housing crisis. This phenomenon refers to the tendency of individuals, particularly homeowners, to oppose new developments in their communities based on fears of potential negative impacts on property values or local quality of life. As a consequence, it creates significant hurdles for builders aiming to expand housing options in desirable neighborhoods, effectively stifling construction.
As highlighted in several studies, the rise of NIMBYism correlates with a marked decline in construction productivity. With builders facing a myriad of local regulations and bureaucratic hurdles, the process of developing new housing becomes intricate and cumbersome. This has resulted in a preference for smaller, bespoke projects over mass-produced homes, which further limits the availability of affordable options in the housing market.
Examining Construction Productivity Trends
Construction productivity in the U.S. has shown a troubling decline since the 1970s, contrasting sharply with advances in other manufacturing sectors. While industries like automotive manufacturing have continued to innovate and become more efficient, the construction sector has stagnated. Researchers attribute this disparity largely to the impact of land-use regulations and NIMBYism, which have led to smaller, less efficient building projects.
The decline in construction productivity also reflects a shift away from large-scale developments, which historically allowed builders to leverage economies of scale. As the data indicates, the share of homes constructed in substantial projects has significantly decreased, impacting the overall efficiency of the housing sector. This decline not only hinders the rapid production of affordable homes but also contributes to higher costs for consumers in the face of increasing demand.
Land-Use Regulations and Their Consequences
Land-use regulations, while often designed to protect community interests and environmental standards, can have unintended consequences that stifle housing production. These regulations impose constraints on developers, limiting the size and nature of new construction projects. As a result, the housing market experiences a reduction in the number of units available, which exacerbates the affordability crisis.
Moreover, these regulations typically favor established homeowners who oppose new developments, thus perpetuating a cycle of NIMBYism. By prioritizing the preferences of current residents, municipalities inadvertently create barriers to entry for prospective homebuyers and those in need of affordable housing. Reducing or reforming these regulations could play a pivotal role in reviving productivity and innovation in the construction sector.
Homeownership Challenges for Young Families
For young families, the dream of homeownership is increasingly elusive due to a combination of rising housing prices and stagnant wage growth. Despite aspirations to own their own homes, many find themselves priced out of the market, leading to heightened stress and uncertainty about their financial future. Contributing factors such as student loan debt, high costs of living, and limited access to affordable housing further complicate this crisis.
Many experts argue that without significant policy reforms addressing the housing market trends, the next generation may be forced to delay homeownership or settle for less desirable living conditions. This situation could deepen socioeconomic divides and perpetuate cycles of poverty, making it essential to explore innovative solutions that prioritize affordable housing availability across diverse communities.
Exploring Solutions to Boost Construction Productivity
To address the ongoing housing affordability crisis, policymakers and industry experts are advocating for strategies aimed at enhancing construction productivity. One promising solution is to streamline regulatory processes, making it easier for builders to navigate land-use regulations while ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards. By adopting a more flexible approach to zoning and development, cities can encourage larger-scale projects that effectively meet community needs.
In addition, fostering industry innovation through investment in technology and materials can significantly improve construction efficiency. Embracing prefabricated and modular building techniques could allow for quicker turnaround times and reduced labor costs, ultimately leading to more affordable homes for buyers. Collaboration between government, builders, and community organizations is essential for creating an environment that supports such innovations.
The Role of Economic Policies in the Housing Market
Economic policies implemented at local, state, and federal levels play a crucial role in shaping the housing market. These policies can either facilitate or hinder access to affordable housing, depending on how they balance the needs of developers, current homeowners, and prospective buyers. For instance, tax incentives for developers who focus on affordable housing projects can spur the construction of much-needed units.
Conversely, restrictive policies that prioritize residents’ opposition to new developments often exacerbate the housing crisis by creating artificial scarcity in desirable areas. As the housing market continues to evolve, it will be critical for policymakers to adopt a holistic approach that considers diverse stakeholder interests while prioritizing the long-term goal of equitable housing access for all.
The Future of Homeownership in America
Looking ahead, the future of homeownership in America hinges on the effective resolution of the housing affordability crisis and increased construction productivity. As global economic conditions evolve, along with demographic shifts in consumer preferences, the housing market must adapt to meet the needs of a changing society. For younger generations, achieving the dream of homeownership may require innovative financing options, cooperative ownership models, or community land trusts.
Ultimately, addressing the barriers to affordable housing will necessitate a concerted effort among local stakeholders, community members, and policymakers. By embracing progressive housing policies and challenging NIMBY ideals, America can move towards a future where homeownership is accessible for all individuals and families, regardless of their economic background.
Community Engagement in Housing Development
Community engagement is vital in the process of housing development and can significantly impact the success of new projects. Involving residents in discussions about new construction initiatives fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among stakeholders while also addressing potential concerns from local communities. When residents feel heard and included, they may be more supportive of new developments, thereby alleviating some of the opposition rooted in NIMBYism.
Moreover, collaborative community planning can lead to innovative housing solutions that reflect the needs and desires of both current residents and future homeowners. Engaging diverse voices in the planning process can yield creative approaches that balance affordable housing production with community standards and priorities, paving the way for a more inclusive and sustainable housing landscape.
Reevaluating Urban Development Strategies
As urban areas continue to grow, reevaluating development strategies becomes imperative for addressing the housing affordability crisis. This involves adopting smart growth principles that prioritize sustainable development and equity in housing availability. By focusing on creating mixed-use neighborhoods that integrate affordable housing options with access to transportation, jobs, and amenities, cities can effectively tackle the complexities of modern housing challenges.
Furthermore, prioritizing adaptive reuse of underutilized buildings and land parcels can unlock new opportunities for affordable housing without the need for extensive new construction. This strategic approach not only preserves urban character but also promotes environmental sustainability by utilizing existing resources to meet current housing demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the housing affordability crisis and its causes?
The housing affordability crisis refers to the growing challenge of obtaining affordable housing for many Americans. Key causes include rising home prices, stagnating wages, and increased land-use regulations that restrict housing development. These regulations, coupled with NIMBYism, have contributed to reduced housing supply and higher costs, making homeownership a significant hurdle for many.
How does NIMBYism impact the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBYism, or the ‘Not In My Backyard’ mentality, significantly exacerbates the housing affordability crisis by opposing new housing developments in local areas. This resistance leads to stricter land-use regulations, limiting the construction of new homes and increasing competition for existing properties, ultimately driving up prices and making affordable housing harder to attain.
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations play a crucial role in the housing affordability crisis by dictating how and where homes can be built. These regulations often limit the size and density of housing projects, which can stifle construction productivity. This shrinkage in project scale leads to fewer homes being developed, contributing to the ongoing affordability issues in the housing market.
How has construction productivity affected the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity has seen a notable decline since the 1970s, which has directly impacted the housing affordability crisis. As regulations increase and projects become smaller, the efficiency of home building decreases. This inefficiency contributes to higher costs for new homes, making homeownership less affordable for many prospective buyers.
What are the challenges of homeownership in the context of the housing affordability crisis?
Homeownership challenges during the housing affordability crisis include the surging prices of homes, combined with stagnant wages and stringent lending criteria that make it difficult for potential buyers to qualify for mortgages. Barriers such as high down payments and a competitive market further limit access to homeownership, especially for younger and lower-income families.
How can understanding housing market trends help address the affordability crisis?
Understanding housing market trends is vital for addressing the housing affordability crisis as it provides insights into pricing dynamics, supply and demand shifts, and the impact of regulations. By analyzing these trends, policymakers can develop targeted solutions that promote affordable housing development, streamline regulations, and foster a more balanced housing market.
What impact does increased construction productivity have on housing affordability?
Increased construction productivity can significantly alleviate the housing affordability crisis by allowing builders to produce homes more efficiently and at lower costs. When productivity rises through innovations and economies of scale, housing prices can stabilize or decrease, enabling more families to afford homeownership.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | Homeownership is increasingly out of reach for many Americans; new home prices have doubled since 1960. |
| Impact of Land-Use Regulations | NIMBY land-use policies have limited the size of housing projects, leading to smaller firms and decreased productivity in construction. |
| Decline in Construction Productivity | Construction productivity fell by 40% from 1970 to 2000, despite overall economic growth. |
| Increase in Small Projects | The share of homes built in large projects has decreased significantly over the years, impacting economies of scale. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are experiencing a massive decrease in housing wealth compared to older generations. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue affecting many citizens across the United States, primarily due to restrictive land-use regulations and a decline in construction productivity. With homeownership increasingly becoming an unattainable dream for many, it is essential to reassess policies that inhibit large-scale housing developments. To alleviate this crisis, a focus on innovative building practices and a shift away from NIMBYism could restore productivity and make housing more accessible. Addressing these barriers not only enhances the economy but also ensures that future generations will not suffer from the same systemic limitations.