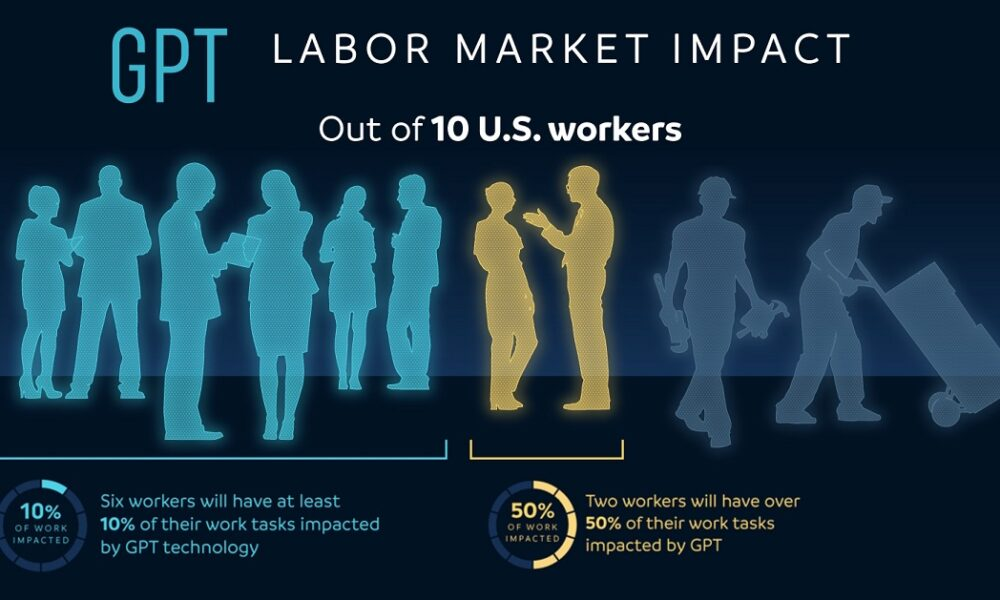
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident, as recent research highlights significant trends in occupational dynamics. A study co-authored by prominent economists investigates the transformative role of artificial intelligence and its potential to induce job disruption across various sectors. With AI’s rapid integration in the workforce, concerns regarding technological unemployment and the economic impact of AI have taken center stage. This evolution is reshaping the landscape of the future of work, emphasizing the need for adaptability and foresight among workers and employers alike. As we explore the depths of these changes, understanding the implications of AI in the labor market will be crucial for navigating the complexities of tomorrow’s economy.
The repercussions of intelligent automation on job markets are becoming a focal point of discussion, as experts analyze how advanced technologies are reshaping employment landscapes. As we delve into the nuances of this issue, terms like technological job disruption and workforce transformation come to the fore. The dynamics of job creation and displacement lead us to consider the broader context of economic shifts and the potential for a drastically different labor environment. This paradigm shift in the workplace requires us to rethink our approach to skill development and workforce engagement in light of emerging AI technologies. To mitigate risks associated with these trends, stakeholders must be proactive in adapting to the shifting tides of employment.
The Impact of AI on the Labor Market
The integration of artificial intelligence into the workforce is transforming job roles and industry standards at an unprecedented pace. Economists are observing significant changes that suggest AI could lead to a major shift in the labor market dynamics. With technologies increasingly automating routine tasks, professionals across various sectors must adapt or risk falling behind. The disruptions caused by AI are reflective of historical technological advancements, such as the introduction of electricity or computers. Each of these advancements has significantly altered the labor landscape, and AI is poised to do the same.
According to a recent study by Harvard economists, the evidence indicates a marked increase in occupational churn due to AI’s influence. As businesses adopt AI-driven processes, there will be a greater demand for high-skilled workers who can navigate these new tools effectively. It highlights a dual-edged sword of technological unemployment, where traditional roles diminish while new opportunities emerge. Employees may need to upskill or reskill to remain relevant, reflecting the ongoing evolution in the economic fabric of the country.
Technological Unemployment and Its Consequences
Technological unemployment has become a pressing concern in the era of advanced AI technology. As machines and algorithms take on tasks previously handled by human workers, entire industries are witnessing a decline in job security. The study elaborates on how roles in low-paid service industries, particularly retail, are being dramatically reduced. The shift to online shopping, accelerated by the pandemic, has positioned e-commerce as a primary beneficiary of AI advancements, pushing out traditional retail jobs and contributing to a more volatile job market.
The potential for job displacement raises critical questions about the future of work and the role of education in preparing the workforce for a technologically driven economy. Individuals will need to cultivate skills in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) to successfully compete in the evolving job landscape. Workers in sectors vulnerable to automation, including retail and administrative positions, must find ways to pivot into roles that leverage AI, positioning themselves for success in a future where technological unemployment becomes increasingly common.
Navigating the Future of Work in an AI-Driven Economy
As AI continues to reshape the workforce landscape, understanding the implications for the future of work becomes crucial for both employees and employers. The recent research highlights four key trends signaling a shift towards a more skilled labor market, particularly in STEM fields. This surge in demand for jobs that require advanced technical abilities signifies a departure from the traditional job polarization that previously characterized occupational growth—now, high-skill roles are rapidly expanding, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
Moreover, as companies leverage AI to enhance productivity, workers in knowledge-intensive jobs must brace for heightened expectations. Firms will likely seek greater efficiency and output, driven by the capabilities AI provides. This reality underscores the necessity for ongoing learning and adaptation in the workforce. By actively engaging in continuous professional development, workers can position themselves advantageously amidst the changing economic landscape shaped by AI technology.
The Economic Impact of AI on Job Distribution
AI’s economic impact extends beyond mere job displacement; it also affects the distribution of jobs across different sectors. The shift towards high-paying skilled jobs indicates a potential reallocation of resources within the labor market. As firms increasingly invest in AI and related technologies, the necessity for workers who can effectively utilize these advancements grows. This trend is shifting the economic landscape, likely resulting in a widening gap between those who can adapt to the new technologies and those who cannot.
The insights drawn from historical data showcase that technology can generate new industries even as it disrupts existing ones. Hence, while some roles may vanish, the advent of AI is also creating unexplored possibilities, driving innovation and entrepreneurship. Thus, navigating the economic impacts of AI requires a balanced approach that considers both the opportunities created and the challenges presented by technological advancements in the labor market.
Preparing for Workforce Changes Due to AI
In light of the rapid changes being introduced by AI, it is essential for educational institutions and organizations to prepare the workforce for upcoming transitions. Lifelong learning and workforce development programs that emphasize technology skills will be paramount in equipping individuals with the necessary tools to thrive. These initiatives should focus on collaborative learning environments where critical thinking, creativity, and technology use are prioritized, ensuring that future workers are ready to meet the demands of an AI-enhanced job market.
Moreover, policymakers must recognize the significance of fostering an adaptive workforce by supporting retraining initiatives and creating transitional programs for those affected by job churn. By investing in education and infrastructure that facilitates skill development in emerging technologies, society can mitigate the adverse effects of technological unemployment and enhance economic resilience in the face of disruption. The collaboration between government, educational institutions, and private sectors is key to preparing a capable workforce for the future.
The Role of AI in Driving Productivity
Artificial Intelligence is redefining productivity standards across various industries, presenting new opportunities for firms to optimize their operations. The evidence gathered by Harvard researchers suggests that increased investment in AI technologies is correlated with heightened productivity levels. Companies embracing AI are not only enhancing their output but also redefining efficiency in ways previously unimaginable, which has become critical amidst global economic shifts.
As businesses leverage AI tools, they are likely to experience transformations in workflow and team dynamics. This transition may lead to a more focused emphasis on strategic decision-making, rather than routine tasks typical in many workplaces. However, while AI can drive productivity, companies must be cautious of over-reliance on automation, ensuring a balanced integration that preserves human oversight and creativity in problem-solving.
Emerging Trends in STEM Careers
The recent data reveals a significant upsurge in demand for STEM jobs as AI continues to redefine career paths within the labor market. The growth in employment opportunities for roles such as software developers and data analysts indicates a broader movement towards technology-driven careers. This shift is opening doors for new entrants into the workforce and reshaping educational priorities towards STEM disciplines, emphasizing the importance of equipping future generations with technical competencies.
Moreover, as businesses increasingly seek individuals skilled in technology, the implication is clear: educational institutions must adapt their curricula to meet these evolving demands. By fostering a culture of innovation and technical expertise, universities and training programs can play a pivotal role in addressing the labor market’s needs, equipping graduates with the skills to thrive in an AI-augmented work environment.
Challenges Amidst AI Integration
While the integration of AI presents numerous benefits, it also introduces challenges that stakeholders must navigate. As industries evolve, workers in traditional roles may struggle to adapt to new technologies, leading to increased job displacement and economic inequality. These challenges highlight the importance of proactive measures that encourage workforce adaptation, such as training programs and policies designed to support vulnerable sectors impacted by automation.
Furthermore, companies must be mindful of the ethical implications of AI deployment, specifically concerning job displacement and fairness in hiring practices. Ensuring diversity and equitable access to opportunities within the rapidly changing landscape is crucial for fostering a sustainable economy. Societal frameworks must evolve in tandem with technological advancements to mitigate potential negative impacts on employment and ensure a balanced transition to an AI-driven future.
AI Empowerment: The Future of Knowledge Work
The advent of AI presents an opportunity for empowerment in knowledge work, challenging conventional roles while enhancing capabilities. The potential for AI to take over mundane tasks allows knowledge workers to focus on higher-value activities, thereby elevating job satisfaction and creative engagement. This shift signifies a transformative phase where human expertise is complemented, rather than replaced, by AI, paving the way for unforeseen innovation within various industries.
As organizations begin to leverage AI’s capabilities, knowledge workers must prepare for a future that demands agility and responsiveness. Embracing AI as a tool to enhance productivity rather than a replacement for human roles is crucial. By fostering collaborative environments where human intellect and AI innovation coexist, companies can unlock new levels of efficiency and creativity, ensuring that workers remain integral to the success of their organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of AI on the labor market and job disruption?
AI’s impact on the labor market is significant, with evidence suggesting it is leading to a shift in job distribution and creating both opportunities and challenges. Research indicates that while some jobs are at risk of displacement, particularly in low-wage service sectors, there is also a growing demand for high-skilled roles in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). As companies increasingly invest in AI technologies, the workforce must adapt to these changes to remain competitive.
How does artificial intelligence contribute to technological unemployment?
Artificial intelligence contributes to technological unemployment by automating tasks traditionally performed by humans. As AI technologies improve, they can replace jobs in various sectors, especially those involving repetitive or low-skilled tasks. The recent trends have shown that while some occupations are declining, there is a rise in demand for jobs that require advanced skills, emphasizing the need for upskilling within the workforce.
What are the economic impacts of AI on workforce distribution?
The economic impact of AI on workforce distribution is profound. AI is reshaping job markets by increasing the demand for high-skilled positions while reducing opportunities in low-skilled occupations. This shift is evident in the decline of retail and service jobs, as e-commerce and automation take precedence. As companies adapt to AI technologies, they will likely seek workers who can leverage these tools effectively, leading to a more polarized labor market.
Will AI change the future of work significantly?
Yes, the future of work will be significantly altered by AI. As AI technologies evolve, they are likely to lead to increased productivity and efficiency but also to the displacement of certain job types. Workers will need to adapt by acquiring new skills, particularly in technology and data analysis, to remain relevant in an AI-driven labor market. This ongoing evolution indicates a shift towards a workforce that is skilled in handling and collaborating with AI systems.
What trends are emerging in the labor market due to AI?
Emerging trends in the labor market due to AI include the end of job polarization, an increasing demand for STEM jobs, a decline in low-paid service work, and a significant reduction in retail sales positions. These trends reflect a shift in job opportunities towards high-skilled positions while low-skilled jobs face greater risks of automation and redundancy. Organizations are actively investing in AI, suggesting that knowledge and technical expertise will be critical for future job seekers.
How should workers prepare for AI’s labor market impact?
Workers should prepare for AI’s impact on the labor market by focusing on continuous learning and skill development. This includes gaining proficiency in areas like data analysis, machine learning, and other technical skills that are increasingly in demand. Additionally, embracing a mindset of adaptability will help individuals navigate the inevitable changes in job roles and responsibilities as AI becomes more integrated into business functions.
What role does upskilling play in addressing AI labor market disruptions?
Upskilling plays a crucial role in addressing AI labor market disruptions by equipping workers with the necessary skills to thrive in a changing job landscape. As many low-skilled positions face the threat of automation, training programs focused on high-demand skills can help displaced workers transition into new roles in technology-driven industries, thereby contributing to a more resilient and adaptable workforce.
What are some examples of AI-driven job changes in recent years?
Recent years have seen notable AI-driven job changes, such as the decline of retail jobs due to the rise of e-commerce platforms utilizing AI for inventory and customer management. Additionally, there has been a notable increase in demand for STEM roles, with jobs such as software developers and data analysts seeing substantial growth. This reflects the broader trend of AI technologies transforming traditional job roles and requiring a shift in the skills workers need.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A new study tracks 100 years of technology’s impact on the U.S. labor market, revealing signs of AI disruption. |
| Between 1990 and 2017, the job market showed stability, challenging beliefs about robots taking jobs. |
| Significant changes began in 2019, indicating the advent of AI as a key driver of labor market evolution. |
| Job polarization is declining; high-skilled jobs are increasing while low-paid jobs struggle to sustain growth. |
| There is a notable increase in STEM jobs, rising from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Low-paid service jobs have seen a decline due to multiple factors including AI, wage increases, and the pandemic. |
| The retail sector has contracted significantly, with retail sales jobs dropping from 7.5% to 5.7% since 2013. |
| Investment in AI is changing the job distribution actively, heralding a shift in workforce skill requirements. |
Summary
The AI labor market impact is becoming increasingly apparent as new research reveals significant shifts in employment patterns. A study by Harvard economists highlights that while earlier decades showed stability, recent years have illustrated consequential changes in job structures and skill demands driven by AI technologies. This evolution is not merely technological but profound in reshaping the landscape of work, questioning the future roles in various industries, and emphasizing the need for adaptation among workers. As AI continues to carve its path in the economy, professionals across all sectors must prepare for a landscape where adaptability and technology proficiency are paramount.